46+ A Particle Of Mass M Rests On A Smooth Plane
A particle of mass m rests on a smooth plane. Web A particle of mass m rests of a smooth plane.

Solved A Particle Of Mass M Rests On A Smooth Plane The Plane Is Raised To An Inclination Angle 8at A Constant Rate A 8 0 At T 0 Causing The Particle To Move Down The
Web A particle of mass m rests on a smooth plane.

. The plane is raised to an inclination angle θ at a constant rate a θ 0 at t 0 causing the particle to move down the plane. Web A ball of mass 5 0 g moving at a speed of 2. The plane is raised to an inclination angle θ at a constant rate a θ 0 at t 0 causing the particle to move down the plane.
The plane is raised to an inclination angle 0 at a constant rate a 0 0 at t0 causing the particle to move down the plane. Determine the motion of the. 0 m s strikes a plane surface at an angle of incidence 4 5 o The ball is reflected by the plane at equal angle of reflection with the.
A particle of mass m rests on a smooth plane. Web A Particle of mass m rests on a plane with no friction. The plane is raised to an inclination angle the Lagrangian and solve Lagranges equation of motion for the particle.
The plane is raised to an inclination angle theta at a constant rate alpha. Web A particle of mass m is constrained to lie along a frictionless horizontal plane subject to a force given by F x kx kx3A2 where k and A are positive constants. At a constant rate a.
The plane is raised to an inclination. Web Find step-by-step Physics solutions and your answer to the following textbook question. The plane is raised to an inclination angle theta at a constant rate alphatheta0 text at t0 causing the.
Web A particle of mass m rests on a smooth plane. 0 at t 0 causing the particle to move down the. The plane is raised to an inclination angle θ with a constant rate α θt0 0 causing the particle to slide.
Web A particle of mass m rests of a smooth plane. The plane is raised to an inclination angle. Web A particle of mass m rests of a smooth plane.
Web The plane is raised to an inclination angle theta at a constant rate alphatheta0 text at t0 causing the particle to move down the plane. Causing the particle to move down. Web A particle of mass m rests on a smooth plane.
The plane is raised to an inclination angle 6 at a constant rate a 6 0 at t 0 causing the particle to move down the plane. Web A particle of mass m rests in a smooth plane.

A Sphere Of Mass M And Radius R Rests On Sufficiently Rough Inclined Plane In Equilibrium As Shown In The Figure Find The Tension In The String
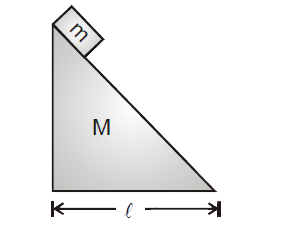
A Particle Of Mass M Is Placed At Rest On The Top Of A Smooth Wedge Of Mass M Which In Turn Is Placed At Rest On A Smooth Horizontal Surface As
Solved A Particle Of Mass M Rests On A Smooth Plane The Plane Is Chegg Com

A Wedge Of Mass M Rests With One Face In Contact With Horizontal Smooth Surface A Particle Of Mass M Is Placed On The Smooth Face On It Inclined

Solved A Particle Of Mass M Rests On A Smooth Plane The Chegg Com

A Wedge Of Mass M Rests With One Face In Contact With Horizontal Smooth Surface A Particle Of Mass M Is Placed On The Smooth Face On It Inclined
A Particle Of Mass M Is Placed At Rest On The Top Of A Smooth Wedge Of Mass M Which In Turn Is Placed At Rest On A Smooth Horizontal Surface As

A Long Plank Of Mass M Rest Upon A Smooth Horizontal Surface A Thin Circular Ring M R Slips Without Rotation Upon The Plank The Coefficient Of Friction Between The Wheel And

A Long Plank Of Mass M Rest Upon A Smooth Horizontal Surface A Thin Circular Ring M R Slips Without Rotation Upon The Plank The Coefficient Of Friction Between The Wheel And

A Mass M Is At Rest On An Inclined Plane Of Mass M Which Is Further Resting On A Smooth Horizontal Plane Now If The Mass Starts Moving The Position Of Centre
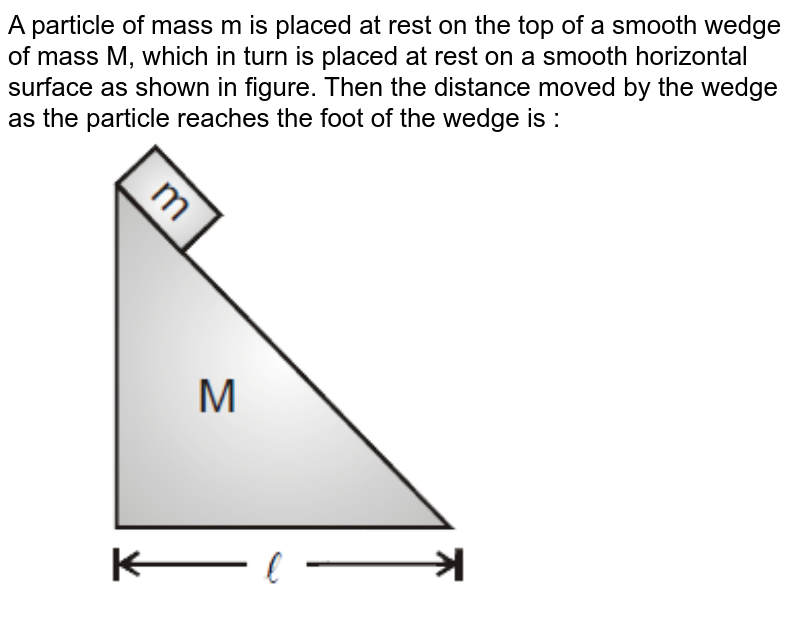
A Particle Of Mass M Is Placed At Rest On The Top Of A Smooth Wedge Of Mass M Which In Turn Is Placed At Rest On A Smooth Horizontal Surface As
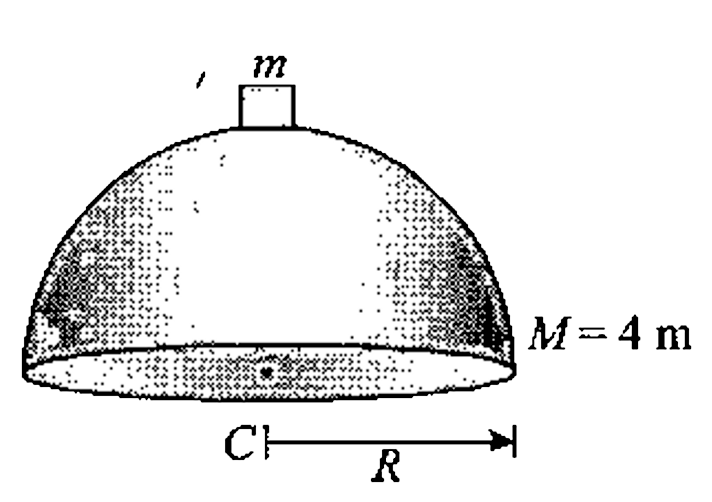
A Small Block Of Mass M Starts Sliding Down From Rest Along The Smooth Surface Of A Fixed Hollow Hemisphere Of Same Mass M Find The Distance Of Centre Of Mass Of

A Plank Of Mass M Rests On A Smooth Horizontal Plane A Sphere Of Mass M And Radius R Is Paced On The Rough Upper Surface Of The Plank And The Plank

A Spring Of Spring Constant K Attached To A Mass M Is Performing An Uniform Circular Motion Of Radius L What Will Be The Extension In The Spring If The Mass Has
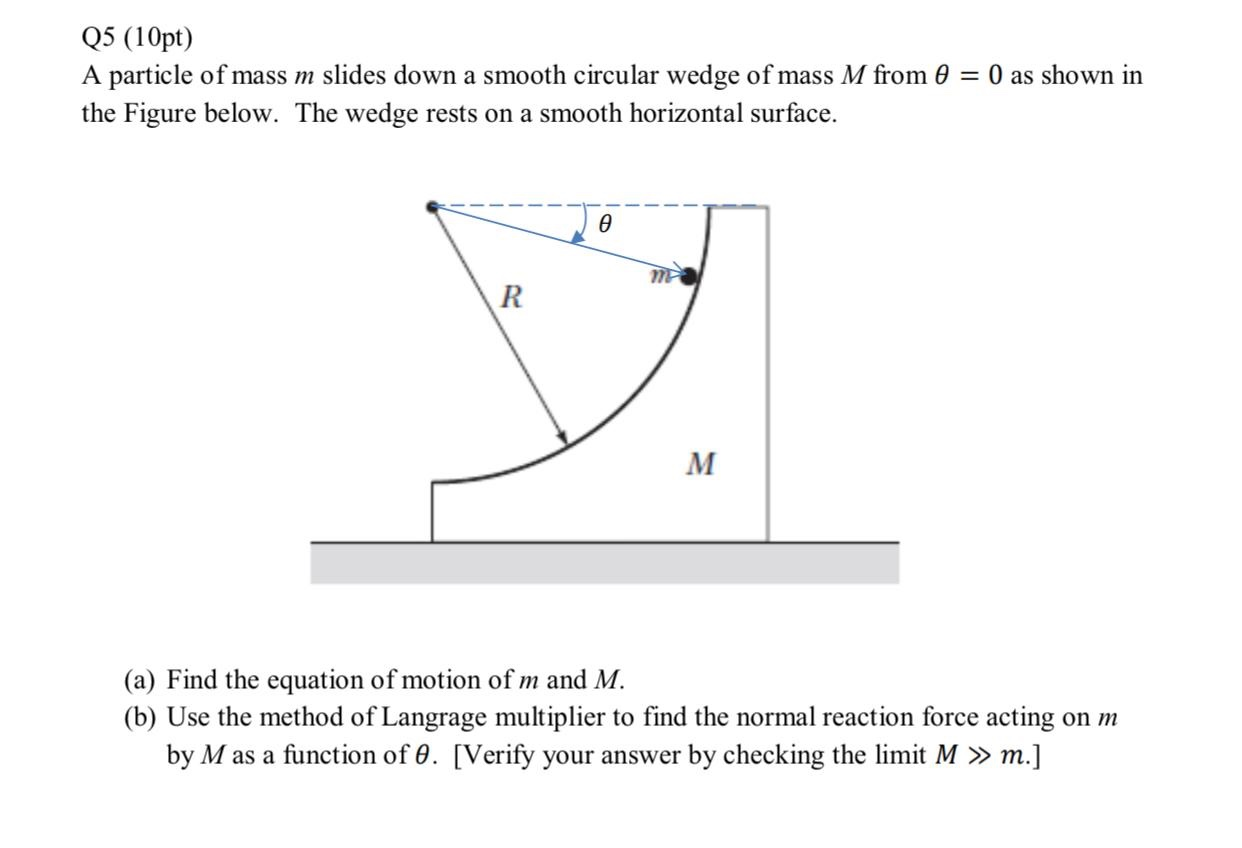
Solved Q5 10pt A Particle Of Mass M Slides Down A Smooth Chegg Com

A Wedge Of Mass M 2m Rests On A Smooth Horizontal In Plane A Small Block Of Mass M Rests Over It At Left End A As Shown In Figure A
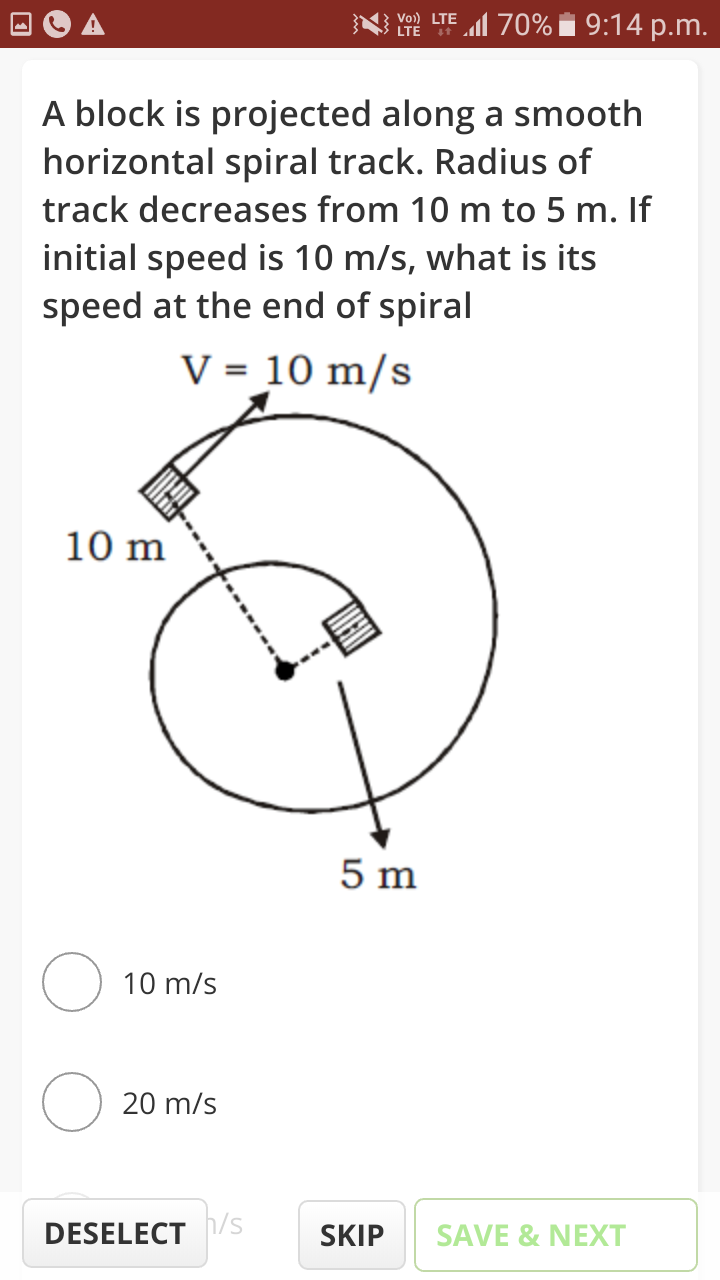
A Particle P Of Mass M Is Released From Rest At Point A On A Curved Smooth Wedge Of Mass M Free To Move On Smooth Horizontal Surface Velocity Of Wedge Sc1smdmm